ZBGIS® Data Update
The aim of updating ZBGIS® data is to verify the existence and correctness of all features and their attributes obtained for a given time horizon and to record changes such as termination of afeature, creation of a new feature or change in the properties of an existing feature. There areprimary and secondarymethods of updating process.
Primary methods:
- photogrammetric method (processing of digital photogrammetric data),
- local investigation (together with the possibility of geodetic surveying of features),
- standardization of geographical names,
- quality control.
Secondary method:
- using data from our own information systems (IS) and IS of other obliged entities (web map services / provided databases).
The updating methods are carried out in particular order. First, the photogrammetric method is used where the operator of the photogrammetric line, using the current airborne imagery (AI), verifies the existence of features, updates the positional situation, adds new features and records selected feature attributes. In this method the positional accuracy depends on the quality of the used AI. This is followed by a local investigation in the field where surveyor verifies the completeness, correctness and existence of features, classification of classes, completes prescribed attributes and newly created features with the possibility of geodetic surveying, according to the valid KTO ZBGIS®. Finally, the updated data will go through a quality control process to determine the suitability of using the data for provision. Quality control checks the position and thematic components of features according torelevant ISO standards. ZBGIS® data quality is defined by the accuracy of geometry, correctnessof attributes, by completeness and flawless topology. Last but not least, the update is influenced by data downloaded from IS of other administrators. Depending on its quality the downloaded data is included in the updating cycle. Data on cadastral district boundariesis entered into the ZBGIS® from our own IS. From this data administrative division (first level of generalization) and reference geodetic points with detailed information are made. These feature classes are updated and verified by another management system and therefore enter the system as trusted and are not subject to quality control.
The method that has been applied to the feature is described in the attribute value of Feature Recognition State (SOI). It also determines the values of general attributes / properties, since the collecting methods of the geometric aspects of features can be geodetic and photogrammetric (the more accurate method always prevails) and they determine the accuracy of the feature's coordinates (horizontal and vertical accuracy). The date when the method was implemented and the reliability of the feature's existence are determined according to the value of the SOI attribute.
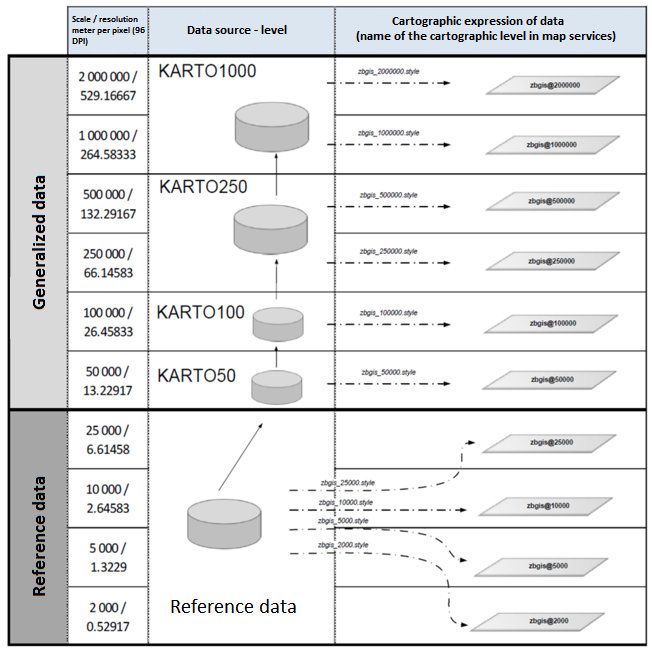
ZBGIS® geodatabase is primarily maintained and managed in ArcSDE v10. It consists of reference data collected and used for scales between 1: 7 000 to 1: 25 000.The reference scale for viewing is 1: 10 000. Generalized data is used for view services in scales from 1: 25 000. For the needs of publishing the services and creating the State Map Series a cartographic representation has been defined for each feature class.